Type 1 diabetes:
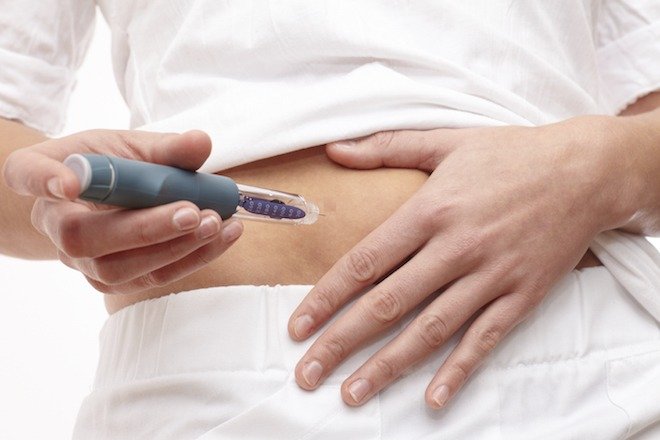
The primary treatment for type 1 diabetes is insulin. Insulin is provided through multiple daily injections or through an insulin pump. Following an active, healthy lifestyle is important in type 1 diabetes, as well as managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Regular monitoring of blood sugar as well as an individual’s carbohydrate intake is extremely important in type 1 diabetes. Currently, type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented or cured.
Type 2 diabetes:
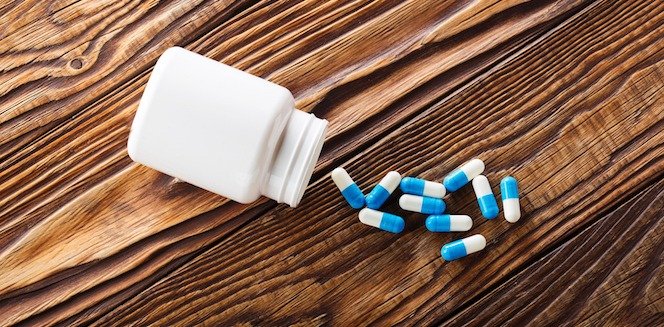
The usual treatment of type 2 diabetes initially involves a combination of both lifestyle changes as well as oral diabetes medications.
Lifestyle changes are very important in the management of type 2 diabetes and include:
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Avoiding/quitting smoking
- Weight loss (if overweight/obese)
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol
While metformin is the most common oral diabetes medication initially prescribed at diagnosis, other classes of diabetes medications include:
- Sulfonylureas
- SGLT2 inhibitors
- DPP-4 inhibitors
- Meglitinides
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
- GLP-1 agonists
Insulin is usually reserved for individuals with a very high A1C who have symptomatic diabetes at diagnosis. It is also used for those who are already on multiple diabetes medications, where the A1C target is still not optimal.
In individuals with prediabetes, following a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, and losing weight can all be effective ways to prevent diabetes. It is important to consult your doctor if you have been diagnosed with prediabetes, to discuss strategies for diabetes prevention.